HIV‐1 capsids mimic a microtubule regulator to coordinate early stages of infection | The EMBO Journal
Overexpression of the microtubule-binding protein CLIP-170 induces a +TIP network superstructure consistent with a biomolecular condensate | PLOS ONE

The microtubule plus-end-tracking protein CLIP-170 associates with the spermatid manchette and is essential for spermatogenesis

AMPK controls the speed of microtubule polymerization and directional cell migration through CLIP-170 phosphorylation | Nature Cell Biology

CLIP‐170 spatially modulates receptor tyrosine kinase recycling to coordinate cell migration - Zaoui - 2019 - Traffic - Wiley Online Library

The microtubule plus-end-tracking protein CLIP-170 associates with the spermatid manchette and is essential for spermatogenesis

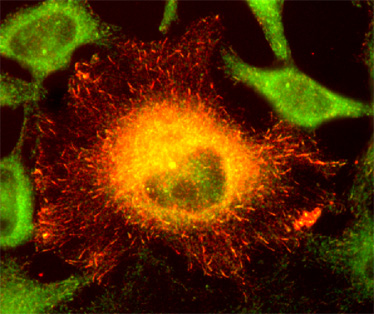
The CLIP-170 N-terminal domain binds directly to both F-actin and microtubules in a mutually exclusive manner - Journal of Biological Chemistry
Model for plus-end tracking activity of mammalian EB1 and CLIP-170. (A)... | Download Scientific Diagram
CLIP-170S is a microtubule +TIP variant that confers resistance to taxanes by impairing drug-target engageme
CLIP-170S is a microtubule +TIP variant that confers resistance to taxanes by impairing drug-target engageme

LKB1 and AMP‐activated protein kinase: regulators of cell polarity - Nakano - 2012 - Genes to Cells - Wiley Online Library

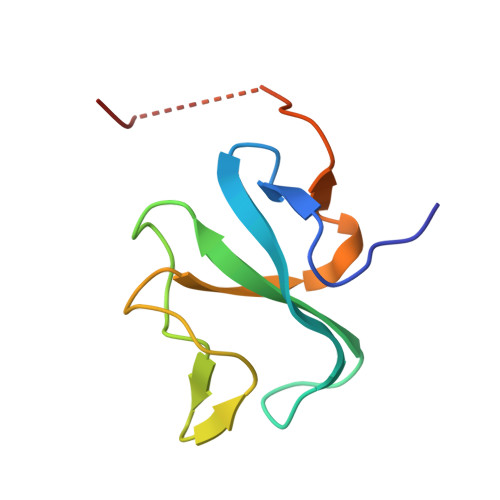
Structural basis for tubulin recognition by cytoplasmic linker protein 170 and its autoinhibition | PNAS

Overexpression of the microtubule-binding protein CLIP-170 induces a +TIP network superstructure consistent with a biomolecular condensate | bioRxiv
Overexpression of the microtubule-binding protein CLIP-170 induces a +TIP network superstructure consistent with a biomolecular condensate | PLOS ONE

Arsenic trioxide disturbs the LIS1/NDEL1/dynein microtubule dynamic complex by disrupting the CLIP170 zinc finger in head and neck cancer - ScienceDirect

Microtubule binding proteins CLIP-170, EB1, and p150Glued form distinct plus-end complexes - ScienceDirect

Structural basis for tubulin recognition by cytoplasmic linker protein 170 and its autoinhibition | PNAS
Potential mechanisms of microtubule plus-end tracking. (A) Motor-driven... | Download Scientific Diagram

CLIP-170S is a microtubule +TIP variant that confers resistance to taxanes by impairing drug-target engagement - ScienceDirect